Air power remains one of the most reliable and efficient energy systems in modern industry, playing a vital role in automotive repair, construction, and manufacturing.
This article explores how pneumatic tools are powered, how compressed air systems work, and how to choose the right air compressor for your needs.
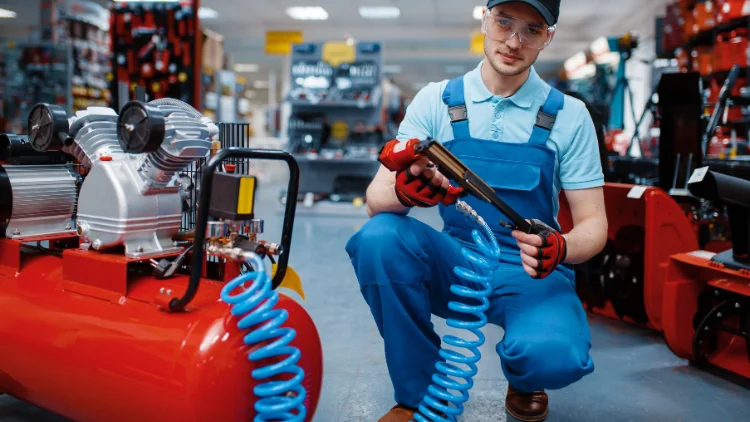

1. What Are Pneumatic Tools?
Pneumatic tools are mechanical devices powered by compressed air rather than electricity or fuel. They transform the energy stored in pressurized air into mechanical motion — allowing them to drill, cut, grind, hammer, or fasten with exceptional efficiency.
These tools are widely used in:
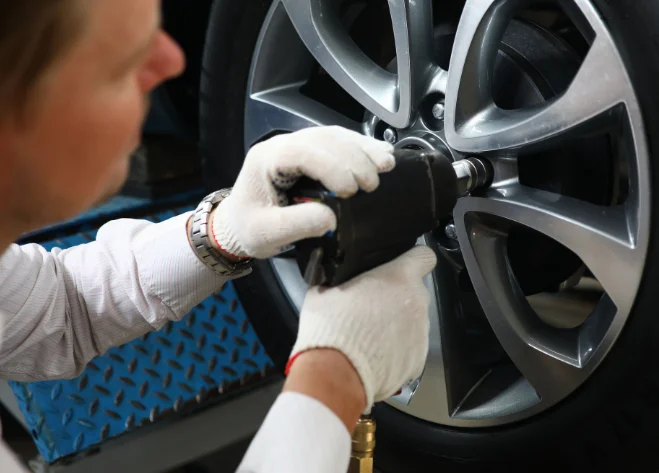
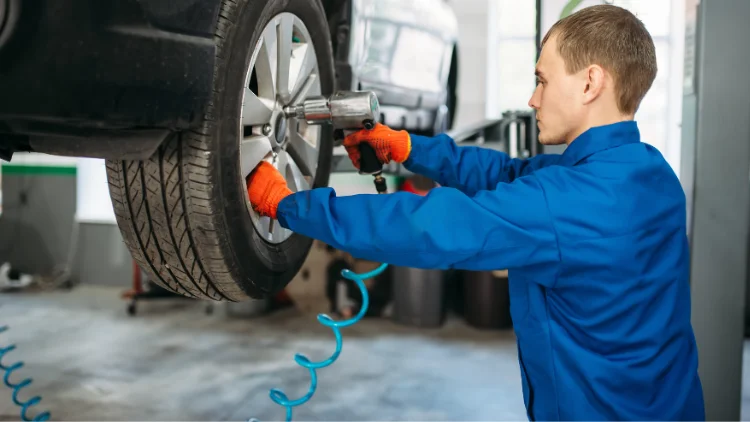
- Automotive repair (impact wrenches, ratchets, tire inflation)
- Manufacturing assembly lines (air drills, screwdrivers)
- Construction (nail guns, chisels, grinders)
- Painting and finishing (spray guns, sanders)
Unlike electric tools, pneumatic models have no built-in motors. This makes them lighter, more durable, and capable of continuous operation without overheating. The result is a tool that can run all day, every day, with consistent torque and precision.
2. What Powers Pneumatic Tools?
The answer is straightforward — compressed air. But the system that delivers that air is a finely tuned combination of pressure, volume, and flow control.
Compressed Air as the Power Source
At the heart of every pneumatic setup is an air compressor. It draws in atmospheric air and compresses it into a storage tank at high pressure (typically 90–120 PSI). When you pull the trigger on a tool, that air is released through a hose, pushing internal components such as pistons or turbines to create motion.
In essence:
Air → Pressure → Motion → Work
The beauty of this system lies in its simplicity and reliability — air is abundant, efficient, and easily controlled.
The Role of the Air Compressor
Air compressors come in several types:
- Piston compressors: Most common for workshops and garages; they use a piston to compress air into a tank.
- Rotary screw compressors: Used in factories for continuous, high-volume air supply.
- Portable compressors: Compact units ideal for small job sites or DIY setups.
The compressor’s job is to maintain a stable airflow that matches the demands of the connected tools. A well-sized compressor ensures that every tool gets consistent pressure without performance drops.
PSI and CFM: The Two Key Numbers
When selecting an air compressor, you’ll often see two ratings: PSI (pressure) and CFM (airflow).
- PSI (Pounds per Square Inch): Measures how much pressure the compressor can deliver.
- CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute): Indicates how much air volume it can supply per minute.
For example:
- A ½-inch impact wrench typically requires 90 PSI and 4–5 CFM.
- A paint sprayer might need 8–10 CFM for smooth, consistent results.
If your compressor can’t provide enough CFM, tools may stall, lose power, or fail to operate at full torque — one of the most common mistakes made by beginners.
3. How Pneumatic Tools Work
The working principle behind pneumatic tools is deceptively simple. When you press the trigger, compressed air flows into the tool’s internal chamber. The rapid expansion of this air pushes pistons or turbines, which convert air energy into mechanical motion.
For instance:
- In an impact wrench, the air spins a hammering mechanism that delivers sudden bursts of torque — ideal for tightening or loosening bolts.
- In a nail gun, compressed air drives a piston that propels the nail instantly into the surface.
Because air tools don’t rely on electric motors, they produce instant torque with minimal heat buildup — making them highly efficient for repetitive or high-torque operations.
4. Pneumatic vs. Electric Tools
So why choose pneumatic tools over electric or cordless ones? The difference lies in efficiency, power density, and reliability.
| Feature | Pneumatic Tools | Electric Tools | Battery Tools |
| Power Source | Compressed air | AC electricity | Lithium battery |
| Weight | Lighter | Moderate | Heavier |
| Torque Output | High and instant | Medium | Limited duration |
| Safety | No sparks or heat | Possible electric shock | Battery overheating |
| Durability | Long lifespan, low wear | Subject to motor fatigue | Shorter lifespan |
| Maintenance | Requires air compressor, oil | Minimal | Battery care |
| Best For | Industrial, heavy-duty | Home & workshop | Remote or mobile tasks |
A pneumatic system can efficiently power multiple tools, delivering steady, instant torque and power while staying cool during long hours of operation — helping prevent downtime caused by overheating.
In contrast, electric tools are more likely to experience heat buildup and performance loss during continuous use.
5. Choosing the Right Air Compressor
To make your pneumatic system work effectively, your compressor must meet the air demand of all connected tools.
Formula:
Total CFM Required = (Sum of each tool’s CFM) × 1.3 (safety factor)
For example:
If you use a 4 CFM impact wrench and a 6 CFM grinder together, you’ll need at least a 13 CFM compressor to maintain stable performance.
Compressor Selection Tips:
- For workshops: 30–60 gallon tank, 90–120 PSI.
- For mobile work: 10–20 gallon portable unit.
- For factories: rotary screw compressor with air dryer and filter system.
Also decide between:
- Oil-lubricated compressors (quieter, longer life)
- Oil-free compressors (cleaner air for painting or food applications)
6. Maintenance and Safety Tips
Pneumatic tools can last decades with proper care. Here’s how to keep them running smoothly:
- Use clean, dry air. Moisture causes corrosion and internal damage. Install a filter and moisture trap if possible.
- Lubricate regularly. A few drops of pneumatic oil before each shift keeps seals tight and parts moving freely.
- Inspect hoses and fittings. Air leaks waste pressure and reduce torque. Replace cracked hoses immediately.
- Drain your air tank daily. Condensation buildup can cause rust inside the compressor.
- Check O-rings and valves. Worn seals can lead to air hissing or pressure loss.
- Never exceed rated pressure. Over-pressurizing a tool or hose is dangerous and voids warranties.
- Wear safety gear. Eye protection and earplugs are essential when working with high-pressure air.
7. Common Problems and How to Fix Them
| Issue | Likely Cause | Solution |
| Tool loses power | Air leak or low PSI | Tighten fittings, check regulator |
| Tool won’t start | Moisture in line | Drain moisture trap |
| Inconsistent torque | Dirty valve | Clean and lubricate |
| Air hissing after use | Damaged O-ring | Replace seals |
| Compressor runs constantly | Leak or low tank capacity | Inspect system for leaks |
Routine checks take minutes but can save hours of downtime.

8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Do Pneumatic Tools Run On?
They run on compressed air supplied by an air compressor. The air’s stored energy is released to drive mechanical movement inside the tool.
Are Pneumatic Tools Stronger Than Electric Ones?
Generally yes. Air tools deliver higher torque and can operate continuously without overheating.
Do Pneumatic Tools Need Oil?
Yes, most air tools require light lubrication. A few drops of oil prevent friction and corrosion.
Can I Use Co₂ or Nitrogen Instead of Air?
You can, but it’s not cost-effective for regular use. Compressed air is cheaper and easier to regulate.
Can Pneumatic Tools Be Used in Hazardous Environments?
Absolutely. Since they generate no sparks, they are ideal for oil, gas, and chemical industries where fire safety is crucial.
What Size Air Hose Should I Use?
Use a ⅜-inch hose for most light tools and ½-inch or larger for high-flow applications to minimize air loss.
9. Conclusion
Pneumatic tools, when paired with the right air compressor, deliver unmatched torque, stability, and safety.Compared with electric tools, they’re built for long hours of heavy-duty operation with virtually no heat fade or performance loss.
From automotive repair to large-scale manufacturing, pneumatic tools remain a cornerstone of modern industry.
Explore the full range of Kafuwell pneumatic tools and air compressor solutions — engineered for precision, durability, and dependable performance to keep your business running at its best.